|
Contact |
|
R20/Consultancy |
|
+31 252-514080 |
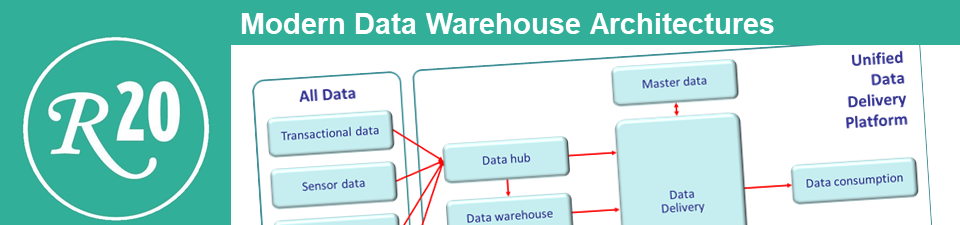
Title: Modern Data Warehouse Architectures: From A - Z
Abstract: There was a time when a data warehouse architecture consisted of a chain of databases all running on one or two machine in our own data center. Handwritten ETL programs were used to copy and transform data from one database to another. But so much new technology offering innovative opportunities has become available, there are so many new BI requirements, and we have new ways to design our data warehouse architectures. Data warehouse architects are struggling with all these new developments. They have to find answers for an almost endless list of questions. Should the data warehouse be developed with Hadoop? Do we still need data marts if the BI tools read data into memory? Can we use Spark as query performance booster? What does it mean to design datavault-based data warehouses? How does data streaming and the IoT work together with the data warehouse? Should we move the entire architecture into the cloud? Can we replace the data warehouse by a data lake? What is the role of the logical data warehouse? Will an analytical SQL database server solve all our query performance problems? And so on, and so on.
This session discusses all the architectural and technical developments. How are they interrelated? How to migrate to a modern architecture? What are the pros and cons of all these developments?
Topics:
1. The Changing World of Business Intelligence
-
Big Data: Hype or reality?
-
Operational intelligence: does it require online data warehouses?
-
Data warehouses in the cloud
-
The shift from IT-based development to self-service BI
-
The business value of analytics
-
The need for modern data warehouse architectures
2. Characteristics of Traditional Data Warehouse Architectures
-
Chain of databases and rigid procedures
-
Initially designed for managed reporting
-
Reports have to be auditable, governable, and must deliver high quality results
-
Inflexible and poor productivity
3. The Influence of New Data Storage Technology on Architectures
-
Are data marts needed when analytical SQL database servers are used?
-
How to incorporate big data technology, such as Hadoop and NoSQL, in BI systems
-
Dealing with schema-on-read data in a BI environment
-
How specialized data storage technology, such as graph databases, can extend analytical power
4. The Logical Data Warehouse Architecture
-
The need for a flexible data warehouse architecture
-
The logical data warehouse architecture is based on the principle of data abstraction
-
Data virtualization servers offers on-demand data integration
5. Data Lakes and Data Scientists
-
How does a data scientist work?
-
Investigative analytics and the data scientist
-
Shortening the data preparation phase through a data lake
-
Physical data lake versus logical data lake
6. BI in the Cloud
-
The pros and cos of moving the data warehouse to the cloud
-
Five levels of unburdening: hardware-in-the-cloud, database-in-the-cloud, data-warehouse-in-the-cloud, BI-solution-in-the-cloud, and BICC-in-the-cloud
-
Is BI in the cloud suitable for fast data and data science?
7. From Operational BI to Fast Data and the Internet-of-Things
-
Analytics at the speed of business
-
Different forms of operational BI: operational reporting, operational dashboarding, operational analytics and embedded analytics
-
What is time-series analysis?
-
Fast data = big data + fast streaming + fast decisions
-
The relationship between the Internet of Things and business intelligence
8. Data Warehouse Automation
-
Building and maintaining data warehouse should not be a manual process
-
Data warehouse automation to create and maintain data warehouses and data marts faster
-
Being able to exploit new technology easier
9. Data Vault for Compliancy
-
Modelling and developing enterprise data warehouses using data vault
-
Data vault leads to highly flexible and integrated data structures and helps to ensure compliancy
-
Using data vault to create more flexible data warehouses
-
What are hub, link, and satelite tables?
-
Using Supernova to make data in the data vault available to a large reporting audience
10. Closing Remarks
You will learn:
-
What the use cases are of Hadoop and Spark in a data warehouse architecture?
-
To distinguish between five levels of BI in the Cloud and how they differ.
-
What the advantages are of using datavault as design technique.
-
Whether data warehouse automation is a hype or reality.
-
How Spark can be used to boost query performance and may even replace data marts.
-
How a logical data warehouse and virtual data lake can work together.
-
How analysis of streaming data can be embedded in a more classic architecture?
-
Why operational BI demands a new architecture.
Geared to:
-
Business intelligence specialists and data warehouse designers who want to know about all the new developments.
-
Data scientists, data analysts, and business analysts who use and work with data every day and who want to know which of all these developments may help them.
-
Technology planners, technical architects, and enterprise architects who need to know how the evaluate all these new developments on their technical merits.
-
Database developers and database administrators who need to know what the impact is of Hadoop and Spark on database aspects.
-
IT Managers who need to be informed about all these new developments to see what the potential business benefits are.
Related Articles and Blogs:
 The Need for Flexible, Bi-Modal Data Warehouse Architectures
The Need for Flexible, Bi-Modal Data Warehouse Architectures
 Predicting the Future of IT is Very Difficult
Predicting the Future of IT is Very Difficult